India stands at a transformative juncture. Rapid urbanization, a swelling population, and the rapid penetration of digital technologies have reshaped the country’s socio-economic fabric.
As progress accelerates, so do the complexities of ensuring safety and stability. Traditional models of security, rooted in physical deterrence and manual vigilance, are fast becoming outdated. In a world marked by evolving threats and rising uncertainty, the need for a smarter, more integrated approach to security is not just important, it is essential.
Evolving threat landscape: urban growth, digital disruption, and new vulnerabilities
The security challenges we face today have grown more complex and layered compared to a decade ago. While traditional concerns like unauthorized physical entry persist, newer vulnerabilities have emerged due to rapid urbanization and technological integration. With India’s cities expanding and smart infrastructure becoming more widespread, the scope of potential disruptions has broadened.
 For example, the contemporary security landscape presents significantly more intricate challenges than it did a decade ago. While foundational security measures—such as perimeter access control and physical surveillance—remain relevant, they are no longer sufficient on their own. The proliferation of smart infrastructure and rapid urban expansion, particularly in Indian metropolitan regions, has introduced new vectors of vulnerability that demand a multi-layered, integrated security approach.
For example, the contemporary security landscape presents significantly more intricate challenges than it did a decade ago. While foundational security measures—such as perimeter access control and physical surveillance—remain relevant, they are no longer sufficient on their own. The proliferation of smart infrastructure and rapid urban expansion, particularly in Indian metropolitan regions, has introduced new vectors of vulnerability that demand a multi-layered, integrated security approach.
In modern urban environments, physical security systems are now deeply intertwined with digital technologies. Smart buildings commonly employ IoT-based devices for access management, environmental controls, and energy optimization.
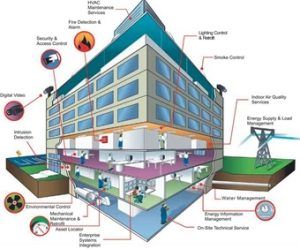 However, this interconnectedness also increases the attack surface for cyber threats. For instance, vulnerabilities in unsecured endpoints such as IP cameras, smart elevators, or HVAC systems can serve as entry points for lateral network intrusions.
However, this interconnectedness also increases the attack surface for cyber threats. For instance, vulnerabilities in unsecured endpoints such as IP cameras, smart elevators, or HVAC systems can serve as entry points for lateral network intrusions.
Furthermore, the deployment of centralized Building Management Systems (BMS) and SCADA frameworks—often integrated with cloud-based dashboards and APIs—requires robust authentication, continuous monitoring, and secure data transmission protocols. The adoption of 5G and edge computing further complicates the security model, requiring real-time threat detection, anomaly analysis, and automated incident response mechanisms.
To address this evolving threat landscape, technical implementation must include:
● End-to-end encryption and secure firmware updates for all IoT devices
● Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA) across internal networks
● AI-powered surveillance analytics for proactive anomaly detection
● Role-based access controls (RBAC) tightly coupled with identity federation services
● Integration of physical and cyber threat intelligence through unified security operations centers (SOC)
The implementation of security must transition from isolated systems to converged, policy-driven architectures capable of handling both digital and physical threat vectors in real time.
 The role of integrated smart security solutions: manpower meets technology
The role of integrated smart security solutions: manpower meets technology
In response to this changing environment, the security industry is moving towards a model where human expertise is enhanced by cutting-edge technology. This integrated approach marries on-ground vigilance with tools like AI-powered video analytics, remote surveillance, automated access control, and digital incident response systems.
For example, a modern security command center at a manufacturing plant can now track movements, identify anomalies, and alert personnel in real-time, using smart AI based algorithms. At the same time, trained security guards on the ground provide human judgment, verification, and quick intervention. This combination of man and machine enables faster, more informed decision-making and limits the scope for error or delay.
 Such a model does not replace the human element but rather augments it and makes the system more reliable, scalable, and responsive to a wide range of threat scenarios.
Such a model does not replace the human element but rather augments it and makes the system more reliable, scalable, and responsive to a wide range of threat scenarios.
Sectoral Impact: Safeguarding Infrastructure, Businesses, and Citizens
Smart security solutions are now playing a pivotal role in enhancing resilience across various sectors. Corporate campuses are adopting biometric and facial recognition systems to control access while protecting employee data and ensuring compliance.
Airports are leveraging AI-based surveillance to streamline passenger movement and manage crowd behaviour. Residential complexes are investing in video door phones, digital visitor tracking systems, and perimeter monitoring.
 In manufacturing and logistics hubs, real-time asset tracking, predictive maintenance alerts, and integrated command centres are reducing both security and operational risks. Public sector utilities, ranging from power distribution centres to water treatment plants are adopting cyber-physical security frameworks to guard against both sabotage and service disruption.
In manufacturing and logistics hubs, real-time asset tracking, predictive maintenance alerts, and integrated command centres are reducing both security and operational risks. Public sector utilities, ranging from power distribution centres to water treatment plants are adopting cyber-physical security frameworks to guard against both sabotage and service disruption.
 More importantly, the focus is shifting from reactive safety to proactive continuity. Today, security is not merely about preventing theft or intrusion, it is about ensuring business continuity, protecting reputation, and building stakeholder trust. Scalable, adaptable solutions are essential for this, especially in a country as diverse and dynamic as India.
More importantly, the focus is shifting from reactive safety to proactive continuity. Today, security is not merely about preventing theft or intrusion, it is about ensuring business continuity, protecting reputation, and building stakeholder trust. Scalable, adaptable solutions are essential for this, especially in a country as diverse and dynamic as India.
In this evolving landscape, no single entity can address all security challenges alone. Building a safer India requires collaboration between government regulators, private security providers, technology innovators, and end-users across sectors. Shared intelligence, common frameworks, and interoperable systems will be the foundation of this collaborative security model.
As we look ahead, the importance of investing in smart, integrated, and future-ready security systems cannot be overstated. These solutions must evolve in sync with emerging threats from cyber warfare to climate-related risks and be rooted in a deep understanding of India’s unique socio-economic realities.
Security must now be viewed as a strategic enabler of growth, not just a reactive safeguard. It is a pillar that supports the broader goals of national development, economic progress, urban resilience, and social stability. In uncertain times, securing the future of India lies in embracing innovation, fostering partnerships, and building a security ecosystem that is as dynamic as the challenges it seeks to overcome.







